What is Polybutadiene?
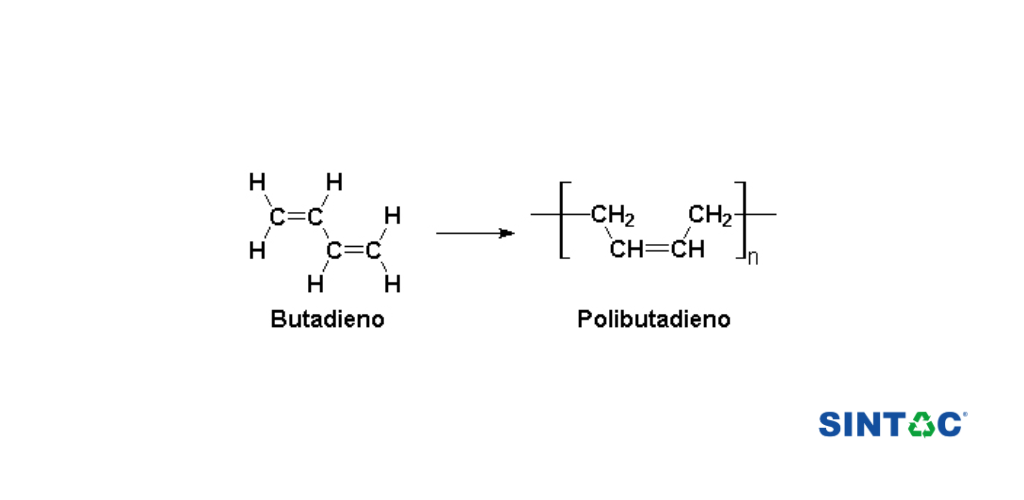
Polybutadiene is a type of synthetic polymer obtained from the polymerisation of butadiene. This polymer is characterised by being highly elastic and resistant, which makes it very useful in different industries.
Types of Polybutadiene:
There are mainly two types of Polybutadiene: high cis Polybutadiene and high trans Polybutadiene.
High cis Polybutadiene is characterized by having a zigzag configuration in its polymer chain, which makes it highly elastic and resistant. It is mainly used in the manufacture of vehicle tires and in the production of rubber products. High-trans Polybutadiene, on the other hand, has a more linear configuration in its polymer chain, making it less elastic and stiffer. It is mainly used in the production of adhesives, coatings and other products that require higher rigidity and strength.
The difference between them lies in the configuration of the carbon atoms in the polymer chain.The difference between them lies in the configuration of carbon atoms in the polymer chain. High cis Polybutadiene has a zigzag configuration and is more elastic, while high trans Polybutadiene has a more linear configuration and is stiffer.
In addition to these two main types, there are also other types of Polybutadiene with different properties and characteristics, which are used in various industrial applications.
What uses does Polybutadiene have?
Polybutadiene is used in a wide variety of industrial applications due to its elastic and resistant properties. Some of the main uses of Polybutadiene are:
- Tire manufacturing: Polybutadiene is a key component in the manufacturing of vehicle tires. Its high elasticity and resistance improve the durability and traction of the tires.
- Production of rubber products: Polybutadiene is used in the production of a wide range of rubber products, such as hoses, gaskets, conveyor belts and other industrial products.
- Adhesives and Coatings: Due to its high strength and durability, Polybutadiene is used in the production of industrial adhesives and coatings.
- Manufacture of plastic materials: Polybutadiene is used as a key ingredient in the production of plastic materials, such as polycarbonate, which are used in the production of bottles, spectacle lenses and other products.
- Paper industry: Polybutadiene is used in paper production to improve the strength and durability of the paper.
Polybutadiene is a versatile and useful material in different industries due to its unique properties. Its high elasticity, strength and durability make it ideal for use in a wide variety of industrial applications.
What are its properties?
Polybutadiene is a strong, elastic polymer that has several unique properties that make it ideal for use in a variety of industrial applications. Some of its most outstanding properties are:
- Elasticity: Polybutadiene is highly elastic and can stretch to several times its original length without breaking. This property makes it ideal for use in products such as tires and rubber products.
- Resistance: Polybutadiene is highly resistant to abrasion, traction and impact, which makes it ideal for use in products that require high durability and resistance, such as tires and industrial adhesives.
- Low glass transition temperature: Polybutadiene has a low glass transition temperature, which means that it becomes more elastic at low temperatures. This property makes it ideal for use in products that need to perform well in extremely cold conditions, such as winter tires.
- Thermal stability: Polybutadiene has excellent thermal stability, which makes it ideal for use in products that must withstand high temperatures, such as industrial adhesives and plastic materials.
- Chemical Resistance: Polybutadiene is resistant to a wide variety of chemicals, making it ideal for use in products that need to withstand exposure to chemicals, such as industrial coatings and adhesives.

Polybutadiene is an elastic and resistant material with unique properties that make it ideal for use in different industrial applications. Its elasticity, resistance, thermal stability and resistance to chemical products make it a highly valued material in the industry.
Production:
Polybutadiene is produced by polymerizing the butadiene monomer, which is a hydrocarbon with four carbon atoms and two double bonds in its chemical structure. Polymerization can be carried out in various ways, depending on the final application of the Polybutadiene and the desired properties.
Butadiene polymerization can be carried out by two main processes: solution polymerization and emulsion polymerization.
In the solution polymerization process, butadiene is dissolved in an organic solvent such as hexane and an initiator is added to start the polymerization reaction. The polymer forms in solution and is then separated from the solvent and purified by evaporation and filtration processes.
In the emulsion polymerization process, butadiene is dissolved in water and an emulsifier is added to form an emulsion. Then, an initiator is added which starts the polymerization reaction and the Polybutadiene is formed into small particles in the emulsion. The particles are separated from the water and purified through drying and filtration processes.
Once produced, Polybutadiene can be modified through vulcanization processes and mixed with other materials to obtain the desired properties for the final application.

What advantages does it have?
Polybutadiene has several advantages compared to other similar materials. Some of the main advantages include:
High strength and durability: Polybutadiene is highly resistant to wear and chemicals, making it ideal for use in demanding industrial environments.
Flexibility and elasticity: the Polybutadiene is highly elastic and flexible, making it ideal for use in applications that require strong, flexible materials.
Low Cost – Polybutadiene is relatively inexpensive compared to other similar materials, making it ideal for your Use in applications where a tough but economical material is required.













